A person drinks Hydrogen Water Before and After Photos (15 minutes elapsed time)
Clumping of the Red Blood Cells can be a non specific indicator of disease. You notice how ALL the cells are stacked? They cannot pass through the tiny opening of the capillaries. This is how many “Sick” RBCs look prior to drinking diatomic hydrogen water.
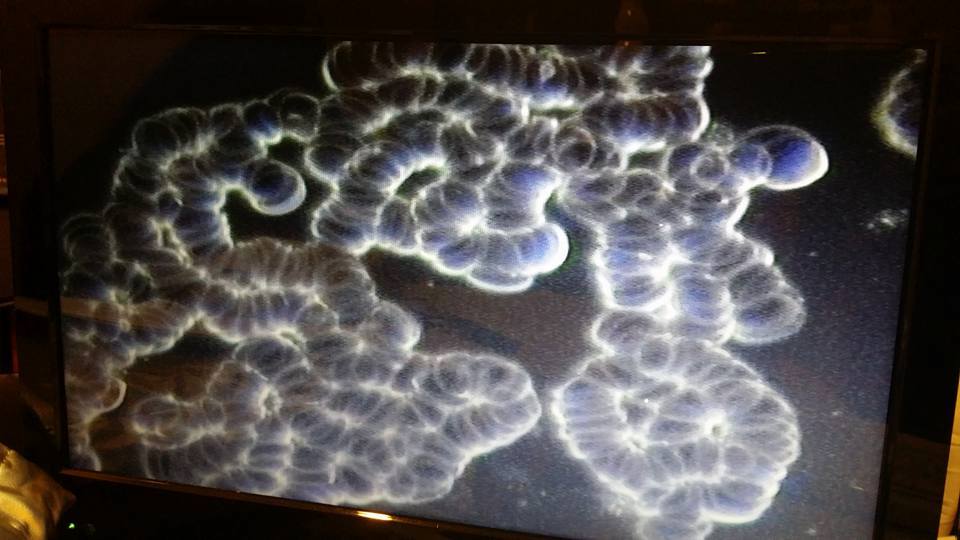
Dark Field Microscope Blood shows Rouleaux before drinking H2 water
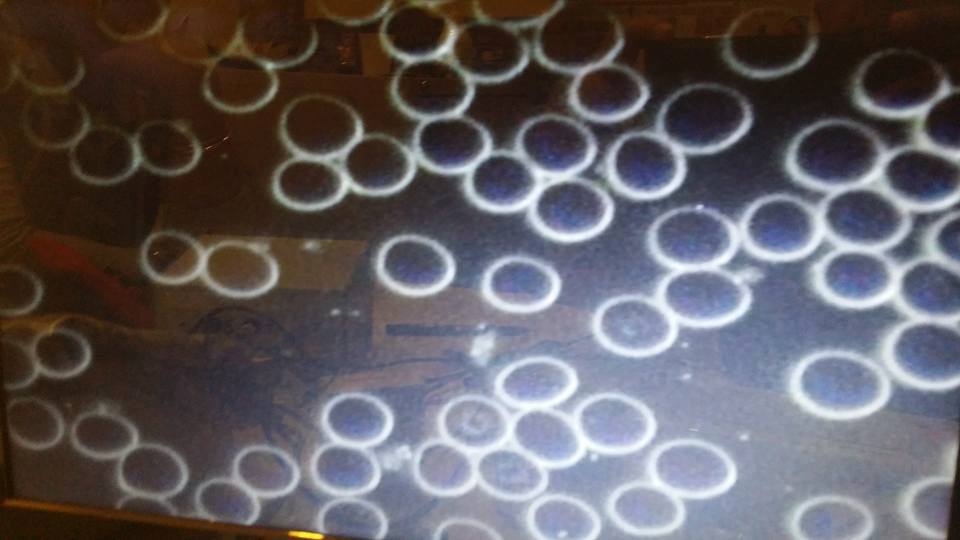

Dark Field Microscope Blood shows Rouleaux after drinking H2 water 15 minutes
What’s the importance of hydrogen water based on these photos? So, you see, tiny capillaries can only accept free flowing singular and independent red blood cells.
Rouleaux are aggregations or clumpings of red blood cells which form because the flat surface of the discoid RBCs gives them a large surface area to make contact and stick to each other. They occur when plasma protein concentrations are high. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases as a result. This is a non-specific indicator of the presence of disease. The presence of Rouleaux is a cause of disease because it will restrict the flow of blood throughout the body.
Thus, you should get the idea in your head that if diatomic hydrogen water can unclump the Red Blood Cells, it will allow an increased flow into the extra cellular fluid. By doing so, it will improve exchange of nutrients including oxygen, and metabolic wastes.
Gwen: How do you know if you have healthy RBC?
Curt: Darkfield microscopy.
Katie: Would increasing water intake making a person well hydrated cause that to happen or is it something specific to H2 water?
Curt: These are photos that Tom posted, the first showing the clumping, the second being taken 15’minutes after drinking hydrogen water. So. If your skeptical friend is correct, and the first photo was due to dehydration and drinking a glass of diatomic hydrogen water unclumped all of the rbc’s in a period of 15 minutes, thus correcting the effects of dehydration, Holy Cow! Right? Drink a glass of regular tap water, you can’t get that effect on severe dehydration! I would say to him, clumping is really not specific to dehydration, but if it corrected it in 15 minutes, all the more reason to drink diatomic hydrogen water!
Katie: From Wikapedia
“Rouleaux (singular is rouleau) are stacks or aggregations of red blood cells (RBCs) which form because of the unique discoid shape of the cells in vertebrates. The flat surface of the discoid RBCs gives them a large surface area to make contact with and stick to each other; thus forming a rouleau. They occur when the plasma protein concentration is high, and because of them the ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) is also increased. This is a non-specific indicator of the presence of disease.[1]
Conversely the presence of Rouleaux is a cause of disease because it will restrict the flow of blood throughout the body because capillaries can only accept free flowing singular and independent red blood cells. The aggregations also known as “clumping” form as an allergic reaction to certain antibiotics and not necessarily because of disease.
Conditions which cause rouleaux formation include infections, multiple myeloma, inflammatory and connective tissue disorders, and cancers. It also occurs in diabetes mellitus and is one of the causative factors for microvascular occlusion in diabetic retinopathy.
Acute-phase proteins, particularly fibrinogen, interact with sialic acid on the surface of RBCs to facilitate the formation of rouleaux. An increase in the ratio of RBCs to plasma volume, as seen in the setting of anaemia and hypovolemia, increases rouleaux formation and accelerates sedimentation. Rouleaux formation is retarded by albumin proteins.”
Katie: So this is very impressive
Shelli: Herman I’m kidding I am intelligent enough to understand all of this and my cousin has a connective tissue disorder–perhaps this would be of some interest to her since she is a Dr. She was just diagnosed.
Disclaimer: This information is not intended to cure prevent or treat any disease. Consult your doctor if you are unwell.
Last Updated on March 29, 2016 by Katie Sisel Distributor
